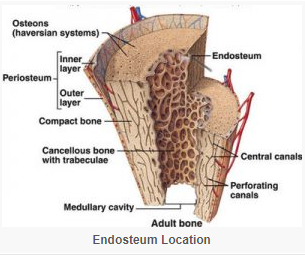
Endosteum
Endosteum is a thin, soft, connective tissue, lining the cavity of long bones like humerus and femur.
It acts as a coating for the inner compact bone and the trabeculae of the spongy (cancellous) bone.
Functions
Bone production
The trilaminar sinus wall is composed of endothelial cells; a thin basement membrane; and adventitial reticular cells that are progenitors of chondrocytes, osteoblasts and adipocytes.
The osteoprogenitor cells of the preosteoblasts present in the endosteum, differentiate into osteoblasts and later on to osteocytes, which are the bone forming cells. They also aid in the formation of bone-matrix secreting cells, also known as bone-lining cells.
The endosteum, along with the periosteum functions for the growth of bone in diameter.
Blood production
Endosteum contains hematopoietic stem cells.