Structure
The bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue found inside certain bones, and it plays a critical role in blood cell production (hematopoiesis). It has a highly organized structure, which can be divided into two main types and several microscopic components:
🩸 1. Types of Bone Marrow
There are two types based on color and function:
A. Red Bone Marrow
-
Function: Actively produces blood cells (hematopoietic).
-
Location: Found mainly in flat bones (sternum, ribs, vertebrae, pelvis) and the ends of long bones in adults.
-
Composition:
-
Hematopoietic cells: Stem and progenitor cells that develop into red cells, white cells, and platelets.
-
Sinusoids: Thin-walled blood vessels that allow mature blood cells to enter the circulation.
-
Reticular (stromal) cells: Provide structural support and produce growth factors.
-
Macrophages: Remove old or defective blood cells.
-
Adipocytes: Fat cells interspersed among hematopoietic tissue.
-
B. Yellow Bone Marrow
-
Function: Primarily stores fat; can revert to red marrow during increased demand (e.g., severe anemia).
-
Location: Found in the shafts (diaphyses) of long bones.
-
Composition: Mostly adipocytes, with a reduced number of hematopoietic cells.
🔬 2. Microscopic Structure
The bone marrow consists of:
| Component | Description / Function |
|---|---|
| Hematopoietic cords | Clusters of developing blood cells around sinusoids. |
| Sinusoids (sinusoidal capillaries) | Large, thin-walled vessels connecting marrow to venous circulation; allow mature cells to exit. |
| Stroma (marrow framework) | Network of reticular connective tissue (type III collagen) supporting hematopoietic cells. |
| Adipose tissue | Provides energy and physical support. |
| Endosteum | Thin layer lining the inner bone surface, containing osteoblasts and osteoclasts. |
🦴 3. Bone Marrow Distribution (Adult)
-
Red marrow: Vertebrae, ribs, sternum, skull, pelvis, proximal ends of femur and humerus.
-
Yellow marrow: Long bone shafts.
🧬 4. Bone Marrow Stem Cell Hierarchy
-
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)
-
Gives rise to all blood cells.
-
-
Myeloid stem cell lineage → RBCs, platelets, granulocytes, monocytes.
-
Lymphoid stem cell lineage → T cells, B cells, NK cells.
+++++++++++++++
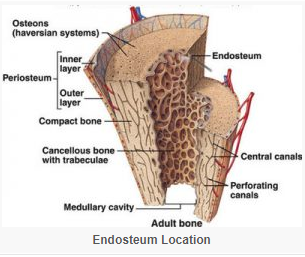
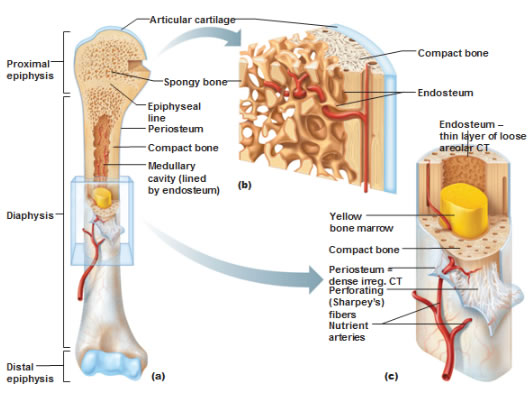
Endosteum is a thin, soft, connective tissue, lining the cavity of long bones like humerus and femur.
It acts as a coating for the inner compact bone and the trabeculae of the spongy (cancellous) bone.
The marrow stroma consists principally of a network of sinuses that originate near the endosteum from cortical capillaries and terminate in collecting vessels that enter the systemic venous circulation.
The trilaminar sinus wall is composed of endothelial cells; a thin basement membrane; and mesenchymal adventitial reticular cells that give rise to osteogenic-adipogenic cells. The endothelium and reticular cells are also sources of hematopoietic cytokines. Hematopoiesis occurs in the spaces between sinuses and is controlled by a complex array of stimulatory and inhibitory cytokines, cell–cell contacts, and extracellular matrix components.
Lymphohematopoietic stem cells can leave and reenter marrow as part of their normal circulation. Their extramedullary circulation can be increased by exogenous cytokines and chemokines.
Within the unique marrow environment, the hematopoietic stem cells differentiate into all the blood cell lineages. Mature cells are produced and released to maintain steady-state blood cell levels. T
The system can respond to meet increased demands for additional cells as a result of blood loss, hemolysis, inflammation, immune cytopenias, and other causes.
++++++++++++++++++++++
The bone marrow is in the medullary canals of long bones and in the small cavities of cancellous or spongy bone.1
+++++++++++++++++++++++++
The bone marrow is a soft, spongy tissue found inside certain bones, and it plays a critical role in blood cell production (hematopoiesis). It has a highly organized structure, which can be divided into two main types and several microscopic components:
🩸 1. Types of Bone Marrow
There are two types based on color and function:
A. Red Bone Marrow
-
Function: Actively produces blood cells (hematopoietic).
-
Location: Found mainly in flat bones (sternum, ribs, vertebrae, pelvis) and the ends of long bones in adults.
-
Composition:
-
Hematopoietic cells: Stem and progenitor cells that develop into red cells, white cells, and platelets.
-
Sinusoids: Thin-walled blood vessels that allow mature blood cells to enter the circulation.
-
Reticular (stromal) cells: Provide structural support and produce growth factors.
-
Macrophages: Remove old or defective blood cells.
-
Adipocytes: Fat cells interspersed among hematopoietic tissue.
-
B. Yellow Bone Marrow
-
Function: Primarily stores fat; can revert to red marrow during increased demand (e.g., severe anemia).
-
Location: Found in the shafts (diaphyses) of long bones.
-
Composition: Mostly adipocytes, with a reduced number of hematopoietic cells.
🔬 2. Microscopic Structure
The bone marrow consists of:
| Component | Description / Function |
|---|---|
| Hematopoietic cords | Clusters of developing blood cells around sinusoids. |
| Sinusoids (sinusoidal capillaries) | Large, thin-walled vessels connecting marrow to venous circulation; allow mature cells to exit. |
| Stroma (marrow framework) | Network of reticular connective tissue (type III collagen) supporting hematopoietic cells. |
| Adipose tissue | Provides energy and physical support. |
| Endosteum | Thin layer lining the inner bone surface, containing osteoblasts and osteoclasts. |
🦴 3. Bone Marrow Distribution (Adult)
-
Red marrow: Vertebrae, ribs, sternum, skull, pelvis, proximal ends of femur and humerus.
-
Yellow marrow: Long bone shafts.
🧬 4. Bone Marrow Stem Cell Hierarchy
-
Pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell (HSC)
-
Gives rise to all blood cells.
-
-
Myeloid stem cell lineage → RBCs, platelets, granulocytes, monocytes.
-
Lymphoid stem cell lineage → T cells, B cells, NK cells.
++++++++++++++++++++++
Functions
Bone production
The trilaminar sinus wall is composed of endothelial cells; a thin basement membrane; and adventitial reticular cells that are progenitors of chondrocytes, osteoblasts and adipocytes.
The osteoprogenitor cells of the preosteoblasts present in the endosteum, differentiate into osteoblasts and later on to osteocytes, which are the bone forming cells. They also aid in the formation of bone-matrix secreting cells, also known as bone-lining cells.
The endosteum, along with the periosteum functions for the growth of bone in diameter.
Blood production
Endosteum contains hematopoietic stem cells.